
David Iben put it well when he said, 'Volatility is not a risk we care about. What we care about is avoiding the permanent loss of capital.' It's only natural to consider a company's balance sheet when you examine how risky it is, since debt is often involved when a business collapses. We note that Ciena Corporation (NYSE:CIEN) does have debt on its balance sheet. But the more important question is: how much risk is that debt creating?
Why Does Debt Bring Risk?
Generally speaking, debt only becomes a real problem when a company can't easily pay it off, either by raising capital or with its own cash flow. If things get really bad, the lenders can take control of the business. However, a more frequent (but still costly) occurrence is where a company must issue shares at bargain-basement prices, permanently diluting shareholders, just to shore up its balance sheet. Having said that, the most common situation is where a company manages its debt reasonably well - and to its own advantage. The first thing to do when considering how much debt a business uses is to look at its cash and debt together.
What Is Ciena's Debt?
As you can see below, Ciena had US$1.54b of debt, at February 2025, which is about the same as the year before. You can click the chart for greater detail. On the flip side, it has US$1.21b in cash leading to net debt of about US$330.6m.
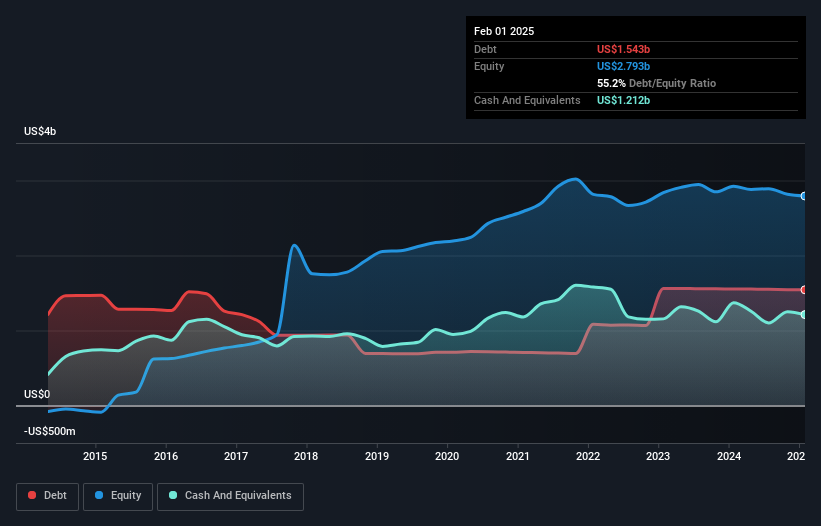
How Healthy Is Ciena's Balance Sheet?
We can see from the most recent balance sheet that Ciena had liabilities of US$956.5m falling due within a year, and liabilities of US$1.82b due beyond that. Offsetting these obligations, it had cash of US$1.21b as well as receivables valued at US$1.08b due within 12 months. So it has liabilities totalling US$490.0m more than its cash and near-term receivables, combined.
Given Ciena has a market capitalization of US$8.55b, it's hard to believe these liabilities pose much threat. However, we do think it is worth keeping an eye on its balance sheet strength, as it may change over time.
Check out our latest analysis for Ciena
We measure a company's debt load relative to its earnings power by looking at its net debt divided by its earnings before interest, tax, depreciation, and amortization (EBITDA) and by calculating how easily its earnings before interest and tax (EBIT) cover its interest expense (interest cover). This way, we consider both the absolute quantum of the debt, as well as the interest rates paid on it.
While Ciena's low debt to EBITDA ratio of 1.0 suggests only modest use of debt, the fact that EBIT only covered the interest expense by 5.2 times last year does give us pause. So we'd recommend keeping a close eye on the impact financing costs are having on the business. Importantly, Ciena's EBIT fell a jaw-dropping 51% in the last twelve months. If that decline continues then paying off debt will be harder than selling foie gras at a vegan convention. There's no doubt that we learn most about debt from the balance sheet. But it is future earnings, more than anything, that will determine Ciena's ability to maintain a healthy balance sheet going forward. So if you're focused on the future you can check out this free report showing analyst profit forecasts.
But our final consideration is also important, because a company cannot pay debt with paper profits; it needs cold hard cash. So it's worth checking how much of that EBIT is backed by free cash flow. Looking at the most recent three years, Ciena recorded free cash flow of 39% of its EBIT, which is weaker than we'd expect. That weak cash conversion makes it more difficult to handle indebtedness.
Our View
Ciena's EBIT growth rate was a real negative on this analysis, although the other factors we considered cast it in a significantly better light. But on the bright side, its ability to handle its debt, based on its EBITDA, isn't too shabby at all. We think that Ciena's debt does make it a bit risky, after considering the aforementioned data points together. Not all risk is bad, as it can boost share price returns if it pays off, but this debt risk is worth keeping in mind. The balance sheet is clearly the area to focus on when you are analysing debt. However, not all investment risk resides within the balance sheet - far from it. For example - Ciena has 1 warning sign we think you should be aware of.
If you're interested in investing in businesses that can grow profits without the burden of debt, then check out this free list of growing businesses that have net cash on the balance sheet.
Have feedback on this article? Concerned about the content? Get in touch with us directly. Alternatively, email editorial-team (at) simplywallst.com.
This article by Simply Wall St is general in nature. We provide commentary based on historical data and analyst forecasts only using an unbiased methodology and our articles are not intended to be financial advice. It does not constitute a recommendation to buy or sell any stock, and does not take account of your objectives, or your financial situation. We aim to bring you long-term focused analysis driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis may not factor in the latest price-sensitive company announcements or qualitative material. Simply Wall St has no position in any stocks mentioned.